
Are your hips or knees causing you so much pain that climbing stairs or just the act of walking has become difficult? Do you hurt when you’re sitting or lying down, or even after trying medications, a cane, and changes in your daily activities?
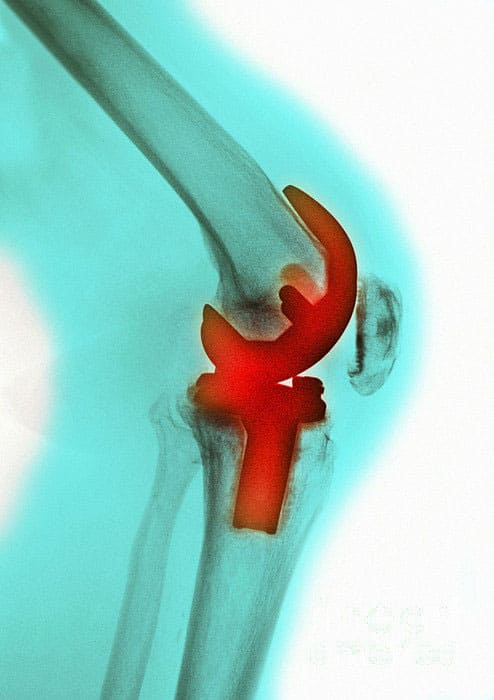
Total knee replacement is a surgical procedure in which injured or damaged parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial parts.
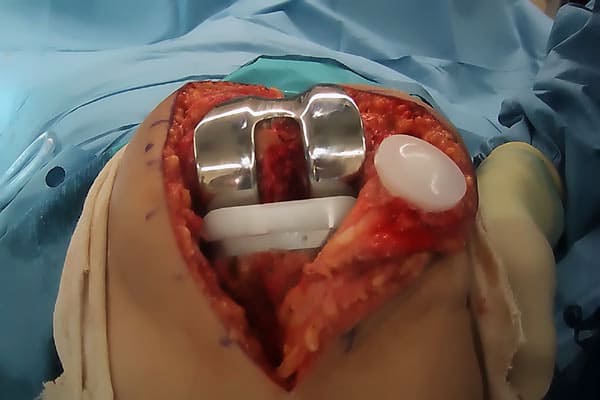
The procedure is performed by opening up the knee capsule and removing the ends of the thigh bone (femur), the shin bone (tibia), and the underside of the kneecap (patella). Artificial parts are cemented into place and make up the new knee joint.
The new knee consists of metal implants on the ends of the shin bone and thigh bone, and a plastic trough in between them.
When do we consider total knee replacements?
Total knee replacement surgery is usually done on people with severe arthritic conditions. It varies from person to person, but you would most likely be considered for a total knee replacement if:
 Pain is severe enough to restrict work, recreation, and/or activities like walking, dressing, and preparing meals
Pain is severe enough to restrict work, recreation, and/or activities like walking, dressing, and preparing meals
You have severe stiffness of your knee X-rays show advanced arthritis or significant deformity of your knee You have daily pain You have significant instability (constant giving way) of your knee.
What can I expect from an artificial knee?
An artificial knee will never work as well as your original knee did before you had arthritis. With pain relief, and good health, you should be able to resume most of your normal activities.
The artificial knee may allow you to return to active sports or heavy labor under your physician’s instructions. Activities that overload the artifical knee must be avoided. About 90 percent of patients with arthritic knees before surgery will have better motion after a total knee replacement.
Many patients do voice difficulty with kneeling after knee replacement. Kneeling will not damage the replacement, but 50% of patients do not like the feel of it.
Total knee replacement is a surgical procedure in which injured or damaged parts of the knee joint are replaced
with artificial parts.
The procedure is performed by opening up the knee capsule and removing the ends of the thigh bone (femur), the shin bone (tibia), and the underside of the kneecap (patella). Artificial parts are cemented into place and make up the new knee joint.
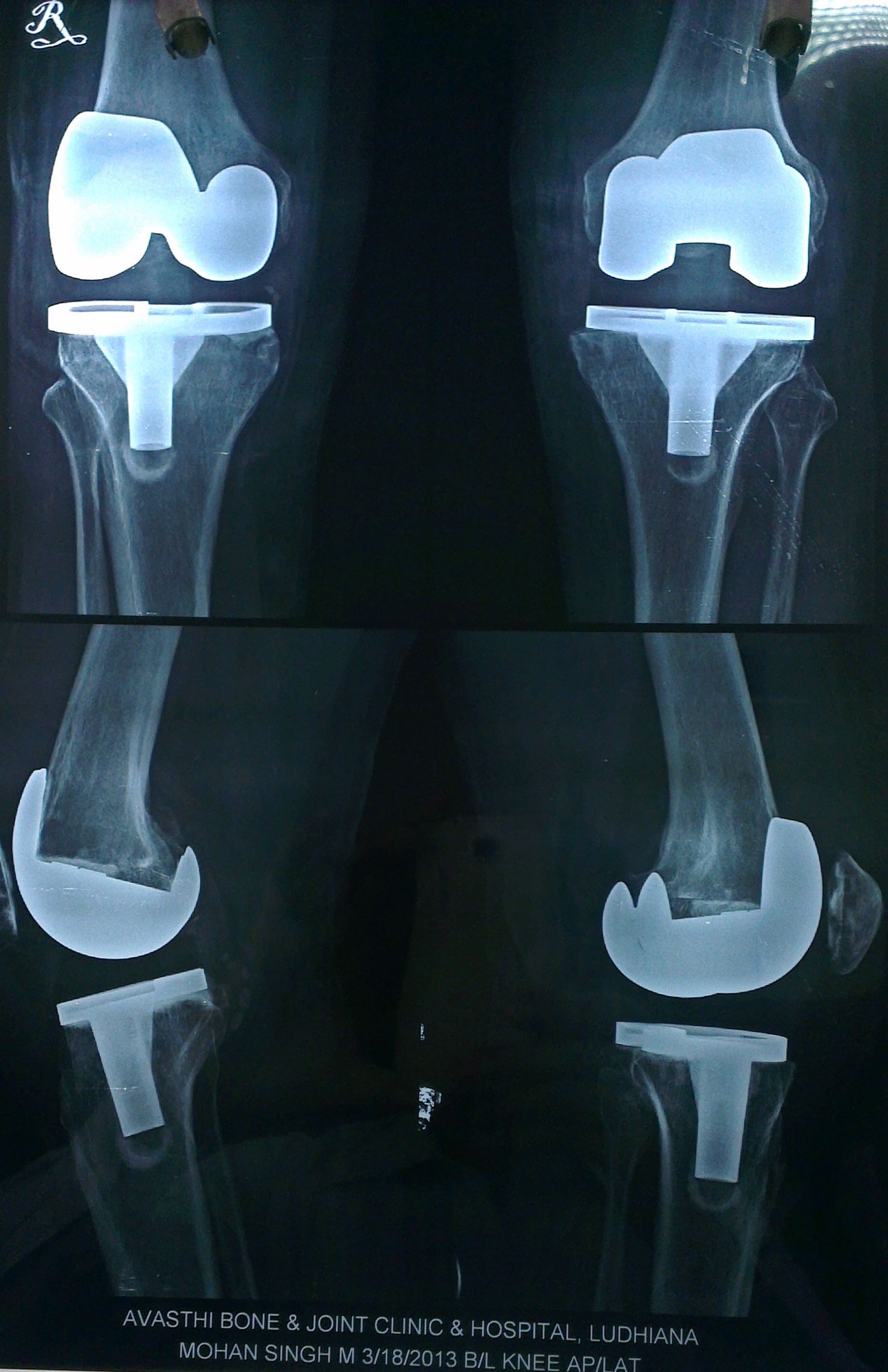
 The new knee consists of metal implants on the ends of the shin bone and thigh bone, and a plastic trough in between them.total knee replacement diagram Cemented into place are metal implants at the top of the shin bone (tibia) and the bottom of the thigh bone (femur). A tray is placed on top of the tibial implant and a button is placed on the underside of the kneecap (patella). Sometimes the patella does not need to be replaced.
The new knee consists of metal implants on the ends of the shin bone and thigh bone, and a plastic trough in between them.total knee replacement diagram Cemented into place are metal implants at the top of the shin bone (tibia) and the bottom of the thigh bone (femur). A tray is placed on top of the tibial implant and a button is placed on the underside of the kneecap (patella). Sometimes the patella does not need to be replaced.
When do we consider total knee replacements?
Total knee replacement surgery is usually done on people with severe arthritic conditions. It varies from person to person, but you would most likely be considered for a total knee replacement if:
Pain is severe enough to restrict work, recreation, and/or activities like walking, dressing, and preparing meals
You have severe stiffness of your knee X-rays show advanced arthritis or significant deformity of your knee You have daily pain You have significant instability (constant giving way) of your knee.
What can I expect from an artificial knee?
 An artificial knee will never work as well as your original knee did before you had arthritis. With pain relief, and good health, you should be able to resume most of your normal activities.
An artificial knee will never work as well as your original knee did before you had arthritis. With pain relief, and good health, you should be able to resume most of your normal activities.
The artificial knee may allow you to return to active sports or heavy labor under your physician’s instructions. Activities that overload the artifical knee must be avoided. About 90 percent of patients with arthritic knees before surgery will have better motion after a total knee replacement.
Many patients do voice difficulty with kneeling after knee replacement. Kneeling will not damage the replacement, but 50% of patients do not like the feel of it.
What are the risks of total knee replacement?
Total knee replacement is a major operation. Complications are rare, but may happen. The most common complications are not related to the knee and do not usually affect the result of the operation. If they occur you may need to stay in the hospital longer than planned. These include:
Complications that affect the knee are less common, but in these cases, the operation may not be
as successful. These complications include:
How do artificial knees stand up over time?
A total knee may last 15-20 years.
Loosening is the major long-term problem. This occurs because the cement crumbles or the bone melts away over time from the wear and tear caused by normal activity.
A loose, painful artificial knee can usually, but not always, be replaced. The results of a second operation are not as good as the first, and the risks of complications are higher. There is an increased risk of wearing your new knee out if you are overweight.